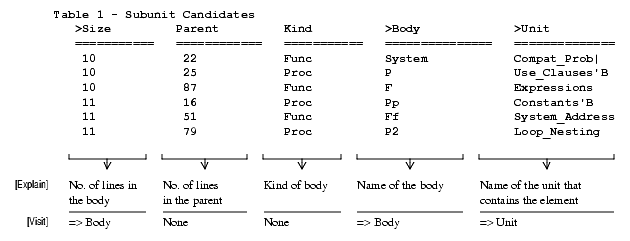
Locate_Subunit_Candidates
This command locates package, subprogram, and task body declarations whose size is greater than some threshold, making them good candidates for subunits. Existing subunits are also located, with their sizes displayed.
Usage Tip: Breaking large units into subunits can improve readability and reduce total compilation time. This command provides information to help decide which units should be subunits and which should not.
Command-Line Interface
Nonstandard Parameters
- Size_Threshold: Specifies the threshold number of lines in a subprogram, over which it would qualify as a subunit candidate.
Sample Output
Subunit Candidates
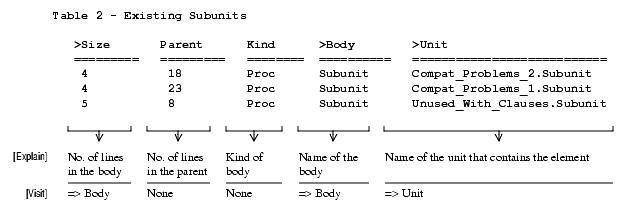
Existing Subunits
Locate_System_Address_Usage
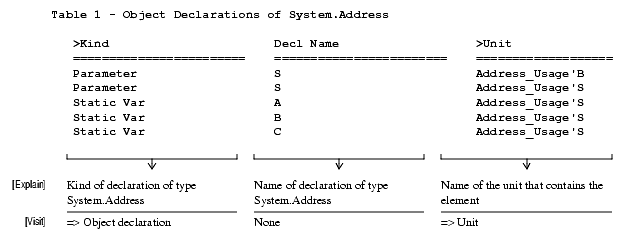
This command locates each usage of the type System.Address, including object declarations and 'ADDRESS attributes. Taking 'ADDRESS of constants and dynamic object declarations, such as parameters and local variable declarations, can be error-prone.
Usage Tip: Using addresses to reference data and performing computations on machine addresses are generally considered error-prone programming styles. Constant values may have no address and dynamic objects such as parameters and local subprogram variables may have addresses that are valid only for a short period of time. This command highlights the use of System.Address within a program.
Command-Line Interface
Nonstandard Parameters
All parameters are standard parameters.
Sample Output
Declarations of System.Address
Use of Address Attributes

Locate_Tasking
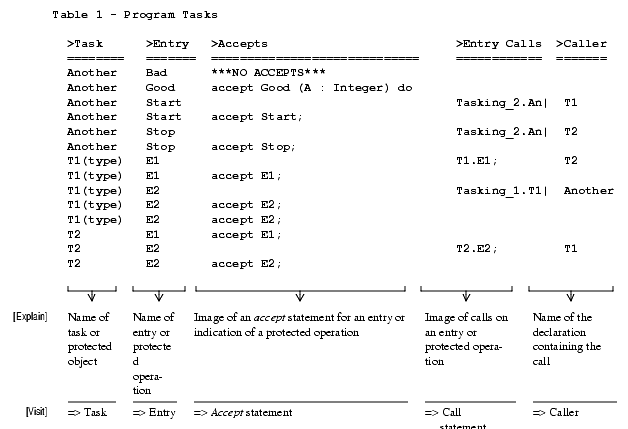
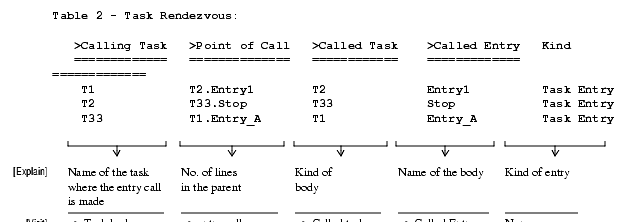
This command locates all tasks, their entries, accept statements of those entries, and other tasks that rendezvous with them through entry calls.
Usage Tip: This command collects and displays all static interactions with tasks. The number and location of all entry calls and the available accept statements can aid in understanding multitasking interactions. Potential errors such as no accepts or no entry calls for an entry can also be seen easily.
Command-Line Interface
Nonstandard Parameters
All parameters are standard parameters.
Sample Output
Task Rendezvous
Locate_Type_Declarations
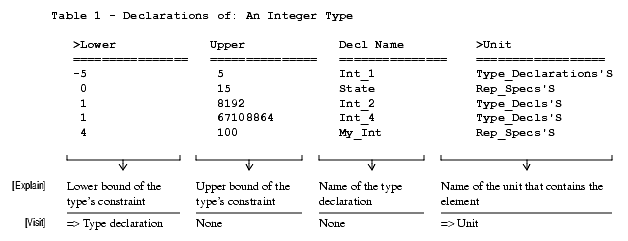
This command locates type declarations and collects attributes about each kind.
Usage Tip: The declaration and use of types is one of the key design aspects of Ada programs. This command helps locate redundant type structures and similar structures that could better be combined into one structure (perhaps a variant record). Some typing standards, for example, require that all subtypes and derived types have constraints. Such standards can be analyzed easily with this command.
Command-Line Interface
Nonstandard Parameters
- Include_*: Specifies whether to include the * kind of type declaration in the hypertable output.
Sample Output
Integer Type Declarations
Subtype Declarations
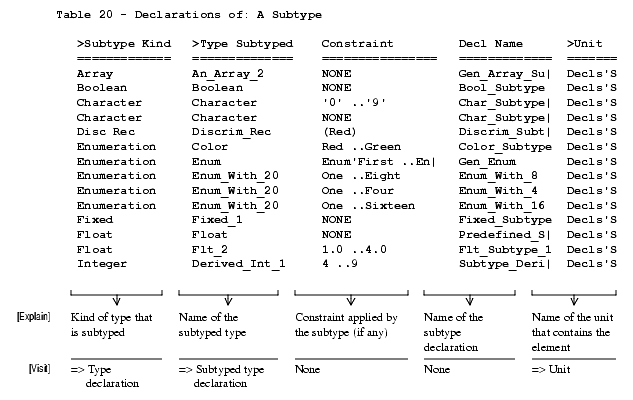
Note: Tables for all other type declaration kinds contain attribute columns relevant to the description of that type declaration.
Locate_Unused_Declarations
This command locates declarations that have no references. This command is similar to the Rational Apex Show_Unused command, but it performs the following additional operations:
- It collects unused declarations in many units at the same time.
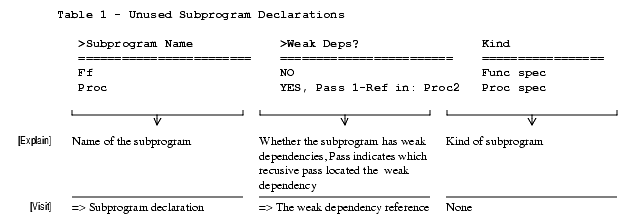
- It filters out "weak" dependencies. If selected, this filtering removes two-part dependencies and dependencies created only by pragmas or representation specifications. The body of a subprogram or package specification is also removed from the list of dependencies. Essentially a weak dependency indicates that the construct can be removed if the second part, pragma, or rep spec is also removed.
Note: To determine whether a declaration is unused or not, the entire closure of a program must be searched. In particular, subsystems that import the subsystem under analysis must be included in the search because those subsystems can have dependencies; a configuration file containing all views in a program should be given for the "Configuration" section of the dialog box. The "Use import closure" button can yield incorrect results, listing declarations as unused when they are in fact used by importing subsystems.
Usage Tip: Declarations can be unused or become unused for many reasons. In most cases (perhaps reusable abstractions excluded), it is a good idea to remove unused declarations and record components from the code. Depending on the compiler implementation, removal of these declarations may reduce code size and will reduce compilation time and increase understandability. Note that because of the filtering of dependencies based on the current imports, some declarations may be unused in the current release but still used in older releases. Care must be taken when removing declarations to maintain release compatibility.
The recursive option can be used to locate strings or groups of declarations that depend on each other but have no outside dependencies
Command-Line Interface
Nonstandard Parameters
- Include_Subprogram_Declarations: Specifies whether to include unused subprograms in the output.
- Include_Type_Declarations: Specifies whether to include unused type declarations in the output.
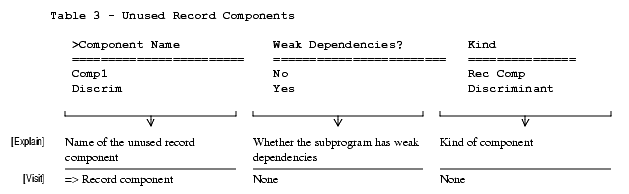
- Include_Record_Component_Declarations: Specifies whether to include unused record components in the output.
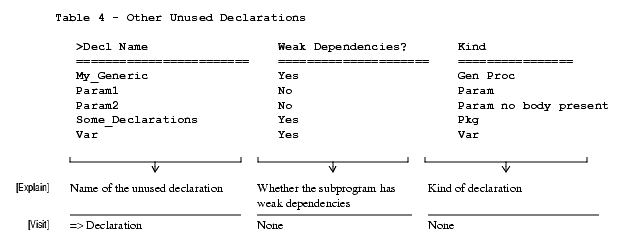
- Include_All_Other_Declarations: Specifies whether to include all other unused declarations in the output.
- Compute_Unit_Dependencies: Specifies how to collect the list of units to traverse for dependencies. Selection of this option will first compute the list of dependent units and then traverse only those units to look for dependencies. Otherwise all units in library are traversed. Use of this option may be more efficient when the user knows that the number of dependent units is small.
- Dont_Filter_Weak_Dependencies: Specifies whether to include weak dependencies (dependencies in pragmas, representation specifications, accept statements, and bodies).
- Recursive: Extends the analysis of unused declarations to locate strings or groups of declarations that depend on each other but have no outside dependencies. This option initiates additional passes through the library. During these passes, dependencies located within declarations that were identified as "unused" in a previous pass are now considered weak dependencies. Thus, if a declaration only has dependencies from other unused declarations, then they form a self-contained group of declarations with internal dependencies but no external dependencies. Analysis continues with additional passes until no new declarations are found that have only weak dependencies.
Sample Output
Unused Subprogram Declarations
Unused Type Declarations
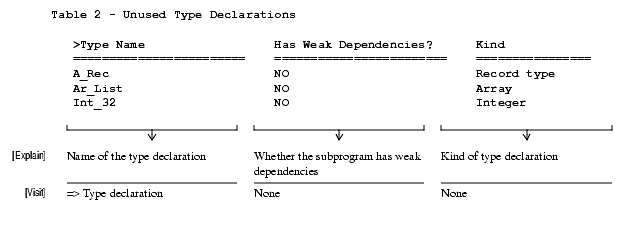
Unused Record Components
Other Unused Declarations
Locate_Unused_With_Clauses
This command locates with clauses that are not used, used only in use or renames clauses, or could be moved from the spec to the body.
Usage Tip: This report identifies units named in with clauses that are unused or misplaced. Such withed units can become unused for many reasons as development progresses, although the reason is usually not obvious to the developer. Their removal can improve code readability and reduce compilation time. More importantly, from an architectural perspective, such references introduce false dependencies that unnecessarily complicate the overall system structure. (Note that the removal of statically unused with clauses, as analyzed in this report, can affect dynamic elaboration order at run-time, perhaps adversely. Where the design calls for such effects, they should be made obvious and portable with a pragma Elaborate.)
Command-Line Interface
Nonstandard Parameters
- Include_Missing_Local_Clauses: Specifies whether to include unit references that have no explicit with clause attached to their immediately enclosing unit. This supports coding standards that require such clauses. It can also be useful in locating where a with clause might be moved if it is not explicitly required by a parent unit.
- Include_Redudant_Clauses: Specifies whether to list repeated with clauses in the report. Since, adding local withs to each unit with an explicit reference will likely result in duplicate with clauses to the same unit, turning this option off can reduce redundant entries in the report.
Sample Output
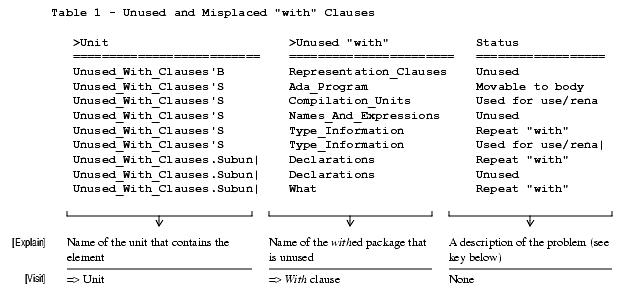
Unused:With is not used in the Ada unit at all
Movable to Body:With is not used in the specification, but is in the body.
Movable to Subunit:With is not used in the body, but is in a subunit.
Repeat "with":With appears more than once in the unit (either in the local program unit or parent unit)
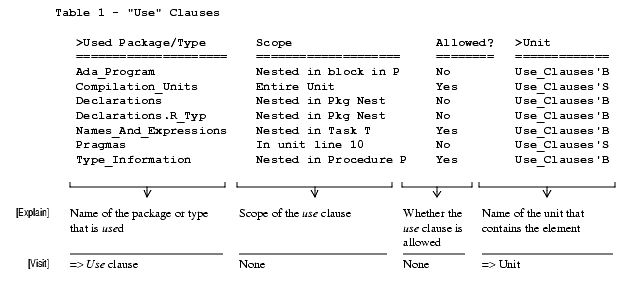
Used for use/rename:With clause is necessary only to compile a use clause, rename clause, or a local pragma Elaborate. Withs used for exported renames are not reported as they may be externally used.Locate_Use_Clauses
This command locates all Ada use clauses in a program. The user can specify names of allowed use clauses in the allowed_use_clauses file in the standards_conformance subdirectory of the current configuration.
Usage Tip: Use clauses generally reduce program readability and increase compilation time because of more complicated name resolution. This command locates all use clauses and displays their context so that decisions can be made about their continued use.
Command-Line Interface
Nonstandard Parameters
- Include_Allowed_Use_Clauses: Specifies whether to include or exclude use clauses whose names appear in the configuration-policy file named standards_conformance/allowed_use_clauses.
- Include_Use_Type_Clauses: Specifies whether to include use type clauses in the hypertable.
Sample Output
Merge_Reports
This command takes as input a set of reports generated by the same Ada Analyzer command and merges them into a single report. This can be useful when the software under analysis is so large that a single invocation of the Ada Analyzer takes too long to complete. In such cases, analysis can be performed on sections of the code (that is, each subsystem or subdirectory) to generate a separate report containing analysis of that subset. A combined report can then be generated with this command.
It is also possible to filter the input tables to create a report whose contents includes only those table entries that match the filtering specification. Details are provided in the description of the Column_Filtering option below. This allows users to reduce the size of reports to contain more specific information. For example, one could use this capability to obtain all information specific to a single unit or set of units from several Ada Analyzer reports.
Usage Tip: This command can be used to combine several reports containing analysis information on several system subsets into a single, sorted report that represents analysis of the entire software system.
Command-Line Interface
Nonstandard Parameters
- Include_Linkage: Specifies whether the linkage information associated with each input report should be transferred to the output report.
- Column_Filtering: Specifies a possibly wildcarded filter string to allow only those column entries that match the filter specification into the output report. The required format for this string option is column_name_filter = contents_filter. If the column_name_filter matches the header of a column, then the contents of that column is matched against the contents_filter. If the column contents matches the filter specification, then that row is placed in the output report. Both the column_name_filter and contents_filter specifications can contain wildcard expressions (`*' matching any sequence of characters, `#' matching any single character). Thus the filter specification "Un* = Sys_*" would place all entries beginning with "Sys_" in columns whose header begins with "Un" in the output report.
- <list of reports>: Specifies a list of reports (.aarpt files) to merge.
Release_Token
This command releases a token so that another user can access the Ada Analyzer. Whenever a user executes an Ada Analyzer command or views a report, a token is requested from the pool of available tokens. A token is not returned to the pool until the user exits Apex or executes this command.
Note: This command can be entered only from a shell window (created from the Tools menu) using the command line: aa release_token. This command takes no options.
Separate_Reports_By_Subsystem
This command will take a set of reports as input, locate all distinct subsystem entries (listed in the SS column), and create one output report for each located subsystem. The names of the output reports are created from the prefix defined by the To_Report_Named parameter followed by a "_for_" <subsystem_name> suffix. The resulting reports will each contain only those entries that refer to that subsystem.
Note: It is possible for reports to be created with no SS column (Display_Subsystem_Name switch => False). In this case, a warning is issued in the command log and no entries entered into the output reports.
Usage Tip: This command can be useful to separate all reported entries for delivery to individual programmers or development teams. It is often the case that software ownership is defined at the subsystem boundary and that reports targeted to each owner are less confusing and more effective.
Command-Line Interface
Nonstandard Parameters
- Include_Empty_Tables - Specifies whether or not to include tables with no entries in the output reports.
- To_Report_Named - The interpretation of this option is slightly different from other commands. In this case, it is the prefix pathname to which "_for_"<subsystem_name> is appended to form the report name for each separated subsystem report.
Visit_Current_Configuration_Policy
This command visits (displays a window containing) the current configuration-policy directory. This can be useful for updating a configuration file or simply viewing which configuration-policy directory is currently active. See the section titled "Determining the Currently Active Configuration Policy" on page 25 for the algorithm used to determine the active configuration.
Note: This command is available only through the Visit Current menu item within the Configuration Policy menu. It is not available from the command line.
Write_To_Ascii_File
This command converts an Ada Analyzer report file into an ASCII file in one of six formats:
- Column Delimited: Each text column is delimited by a specified character. This format is useful as input into database or spreadsheet utilities for further analysis of the report contents.
- Formatted Columns: Each text column is formatted to align properly with each column made as wide as necessary to accommodate the widest entry. This format is the easiest for users to read.
- Frame MIF: Report content is embedded in FrameMaker MIF statements so that it can be imported as a FrameMaker document. Users may then manipulate the document with FrameMaker and print the results.
- Interleaf AIF: Report content is embedded in Interleaf AIF statements so that it can be loaded as an Interleaf document. Users may then manipulate the document with Interleaf and print the results.
- Rich Text Format (RTF): Report content is embedded in Rich Text Format so that it can be uploaded into most PC word processing tools.
- HTML Format: Report content is written is HTML suitable for reading by on-line browsers.
Note: The GUI also provides this capability with the SaveAs command. This description is intended only for command-line users.
Usage Tip: Current database tools can be used to correlate report contents and perform statistical analysis. Use of the FrameMaker MIF format is currently the only method to print PostScript-quality images of a report.
Command-Line Interface
Nonstandard Parameters
- Formatted_Columns_Format: Specifies that the resulting ASCII file should be generated so that each column aligns properly.
- Frame_Mif_Format: Specifies that the resulting ASCII file should be in FrameMaker MIF format so that it can be opened with FrameMaker or FrameViewer. Note that only one format option should be used at a time. The last option specified in the command line will take precedence.
- Interleaf_Iaf_Format: Specifies that the resulting ASCII file should be in Interleaf AIF format so that it can be opened with Interleaf. Note that only one format option should be used at a time. The last option specified in the command line will take precedence.
- Rtf_Format: Specifies that the resulting ASCII file should be in Rich Text Format (RTF) so that it can be opened with PC word processing programs. Note that only one format option should be used at a time. The last option specified in the command line will take precedence.
- Html_Format: Specifies that the resulting ASCII file should be in HTML Format so that it can be opened with internet browser programs. Note that only one format option should be used at a time. The last option specified in the command line will take precedence.
- Column_Delimiter: Specifies the character to use when delimiting columns. This parameter has no meaning when the Formatted_Columns_Format or Frame_Mif_Format parameter is selected.
- Sort_On_Column: Specifies that each table in the report should first be sorted on the specified column before it is written to the output file. If the specified column is not present in a table, a warning is issued and no sorting is performed. The default (0) also indicates that no sorting should be performed.
- New_File: Specifies the name of the output file. If no name is provided, _column_delimited, _formatted, or .mif will be appended to the existing report name depending on the selected format option.
| Rational Software Corporation
http://www.rational.com support@rational.com techpubs@rational.com Copyright © 1993-2000, Rational Software Corporation. All rights reserved. |